Optical polishing and quality control of polished components
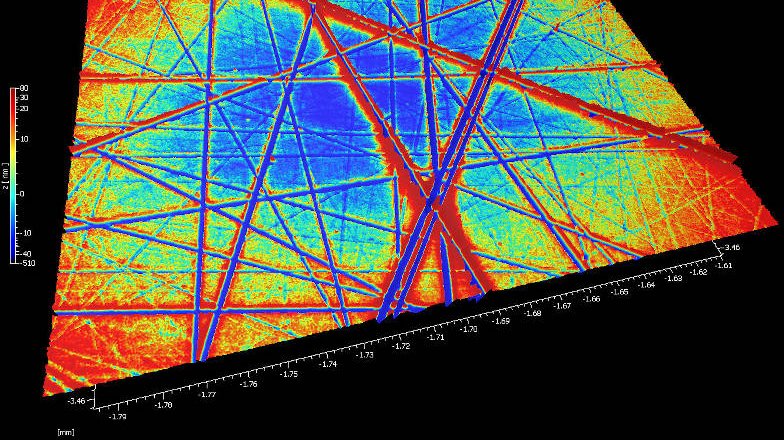
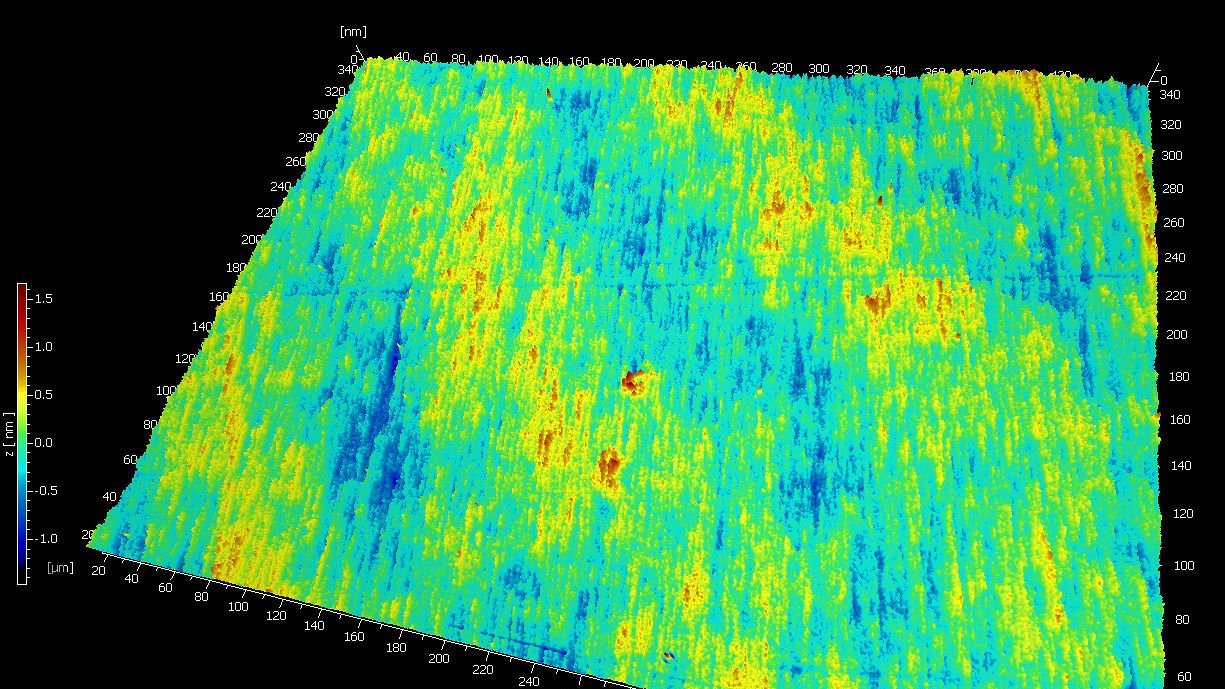
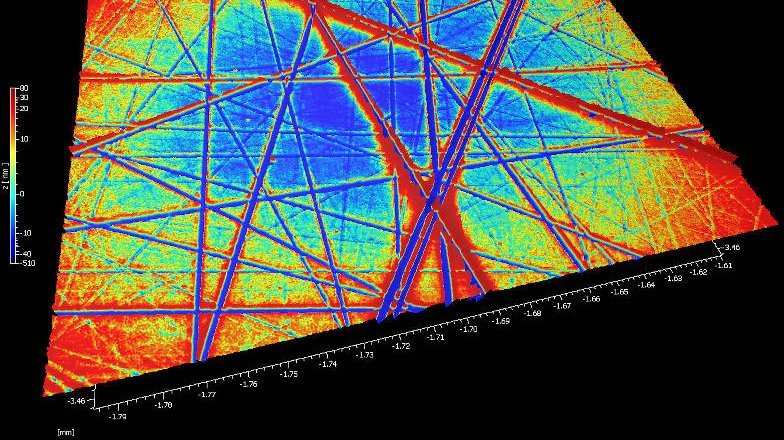
Optical polishing is a fabrication technique widely adopted for the manufacturing process of high precision mechanical and optical components where there is a demand for minimal defects and smooth micro-roughness values. Optical polishing is a method for receiving a superfinish or microfinish of surfaces necessary for further processing, long-term quality and functionality. High precision optical components are made from many materials from glass through to metals. The components manufacturing process are finished with a polishing process in order to meet optical surface finish requirements.
Each manufacturer will have small variations on this basic method of polishing, as well as proprietary techniques to achieve specific goals. For example, different material parameters will behave differently to different spindle / lap speeds. What is the consistency of the small abrasive particle sizes within the slurry that flows over the optical surfaces? How does time affect the polishing process and are larger particles / outside contamination causing scratching, imperfections or damage to the surface?
In short, many surface parameters have an effect on the outcome of the quality on the final surface topography.
Characterizing surfaces of optical components in free feasibility study?
Application note: Quality control in optical polishing
Polishing is a manufacturing technique for refining the surfaces of precision mechanics or optical components. Free-moving grains in a liquid polish the surface with the aim of minimizing surface defects and roughness. Find out here how white light interferometers help to ensure this quality and optimize the production process.