MEMS 在生物医学领域的特性解析与应用拓展
MEMS(微机电系统)与微结构技术,是生物医学领域关键的基础与交叉技术。其应用广泛,涵盖芯片实验室快速诊断、助听器 MEMS 麦克风,以及医学成像超声换能器等,有力推动该领域创新发展。
测定医用 MEMS 传感器和执行器的表面形貌及动态特性极为关键。德国 Polytec 公司基于显微镜的非接触式光学测量技术,可在不接触情况下,利用显微镜高分辨率,精准获取微观信息、监测动态特性,为 MEMS 性能研究提供数据支撑。
在仿生学领域,该振动测量技术也发挥重要作用,用于自然到人工技术系统的 “技术转移” 研究。比如通过测量昆虫听觉生物力学特性,助力开发新型生物医学设备和技术 。

微机械超声换能器助力医学成像新突破
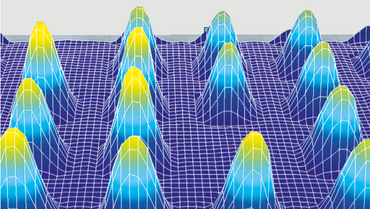
在医学成像领域,尤其是超声检查、血管内超声(IVUS)以及超声心动图等应用场景中,微机械超声换能器(压电式微机械超声换能器 pMUTs 和电容式微机械超声换能器 cMUTs)正发挥着至关重要的作用,不断拓展实时三维医学成像的边界。
要想深入了解这些换能器元件的微机械特性,就需要在高频(约 10 MHz)和高空间分辨率(小于 1 μm)的条件下进行精确测量。这是因为高频环境能够更清晰地捕捉到微小组织的细节信息,而高空间分辨率则可以确保对换能器元件的细微结构和动态变化进行精准监测。
德国 Polytec 公司的显微式激光测振仪在这一过程中展现出了卓越的性能。它提供了多种先进的测量功能,能够以极高的精度为 pMUT 和 cMUT 的研发工作提供关键信息。而且,该测振仪采用非接触式测量方式,避免了对换能器元件造成物理损伤,确保了测量结果的准确性和可靠性,为医学成像技术的进一步发展提供了有力支持。

声子表面声波器件的研发
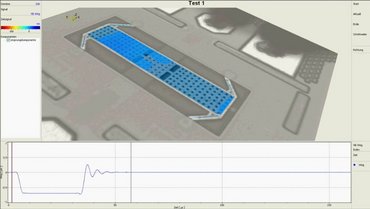
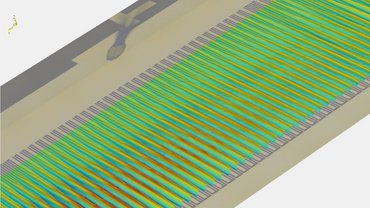
声子表面声波器件在推动集成式即时诊断技术发展方面展现出了极大潜力。其工作原理是借助声音所携带的机械能,在低成本微芯片上对患者的液体样本进行精准处理。科研人员已成功运用声滤波器,实现了从极少量指尖血中检测疟疾的突破,相关成果发表于 [Reboud J. 等人,《美国国家科学院院刊》,2012 年,第 15162 - 15167 页]。
在声子表面声波器件的研发进程中,激光振动测量法发挥着不可或缺的作用。该方法能够直观呈现整个微芯片表面的真实振动状态,为设计方案的有效性提供有力验证依据。展望未来,这一技术平台将进一步集成更为复杂的检测手段,用于肺结核等疾病的精准检测,助力全球公共卫生事业迈向新高度 。